As the leaves change color and the air turns crisp, fall brings with it a host of delights—cozy sweaters, pumpkin spice lattes, and picturesque landscapes. But for many, this beautiful season also ushers in an unwelcome guest: seasonal hair shedding. Before you start blaming your hairbrush or stressing out, let’s delve into what seasonal hair shedding in fall really is, how it works, and most importantly, how you can tackle it head-on.
What is Seasonal Hair Shedding?
Seasonal hair shedding, also known as seasonal hair loss or telogen effluvium, is a natural and temporary phenomenon where you experience an increased amount of hair loss during certain times of the year. In the case of fall, it’s a response to environmental and physiological changes.
How Does it Work?
Our hair growth cycle consists of three main phases:
- Anagen phase: The active growth phase, where hair follicles produce new hair.
- Catagen phase: A transitional phase between growth and rest.
- Telogen phase: The resting phase, during which hair is no longer actively growing and is most likely to shed.
Understanding the Fall Connection
Several factors contribute to fall being a common time for seasonal hair shedding:
1. Seasonal Changes: The transition from summer to fall often involves a drop in temperature and a decrease in sunlight exposure. These changes can affect your hair follicles’ growth cycles.
2. Hormonal Fluctuations: Changes in sunlight and temperature can influence hormone levels in your body. Hormones play a significant role in regulating the hair growth cycle, and fluctuations can trigger shedding.
3. Nutritional Factors: Seasonal variations in diet and nutrient intake can impact hair health. A lack of certain nutrients during the fall season may contribute to hair shedding.
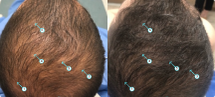
Tips to Combat Fall Hair Shedding
Now that we understand what seasonal hair shedding is and why it happens let’s explore some practical tips to help you combat it and maintain healthy locks during the fall:
1. Balanced Diet: Ensure you’re getting a well-balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and proteins essential for hair health. Consider adding foods like leafy greens, nuts, and fish to your meals.
2. Hydration: Staying hydrated is crucial for overall health, including hair health. Aim to drink enough water daily.
3. Hair Care Routine: Use a mild, sulfate-free shampoo and conditioner suited for your hair type. Avoid overwashing, as it can strip your scalp of natural oils.
4. Gentle Styling: Minimize the use of heat styling tools and tight hairstyles that can stress your hair and scalp.
5. Scalp Care: Massaging your scalp can stimulate blood circulation, promoting hair growth. Consider using a nourishing oil like coconut or argan oil for a soothing scalp massage.
6. Stress Management: Practice stress-reduction techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises, as stress can exacerbate hair shedding.
7. Consult a Professional: If hair shedding persists or becomes excessive, consult a dermatologist or healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation. It could be a sign of an underlying issue that needs attention.